Types Of Hearing Loss
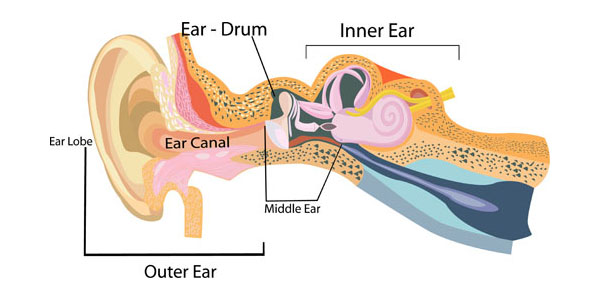
The auditory pathway processes sound information as it travels from the ear to the brain so that our brain pathways are part of our hearing.
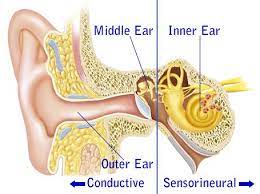
CONDUCTIVE HEARING LOSS
Hearing loss is caused by something that stops sounds from getting through the outer or middle ear. This type of hearing loss can often be treated with medicine or surgery. A decrease in the strength of a sound is called attenuation. Sound attenuation is precisely the result of conductive hearing loss. Whenever a barrier to sound is present in the outer ear or middle ear, some loss of hearing will result.
SENSORINEURAL HEARING LOSS
Hearing loss occurs when there is a problem in the way the inner ear or hearing nerve works.
MIXED HEARING LOSS
Hearing loss includes both conductive and sensorineural hearing loss.
NOISE-INDUCED HEARING LOSS
- Acute noise-induced hearing loss – high levels of continuous or intermittent noise for seconds to hours
- Chronic noise-induced hearing loss- irreversible cochlear hearing loss.
PRESBYACUSIS
Age-related (over 50 years old) symmetrical SNHL, speech recognition is more affected than pure tone.
